Hi guys, It's Kest again. I have taken the time to explain how you can Read and Create DATA over the internet using the HTTP package in Flutter.
what if I tried to post and I make a mistake? you know there is a cliche about making mistakes, it says
"no one is above mistakes".
You wonder how it was possible for you to edit your Posts and Comments on some of your social media applications. Wonder no more 😉😉
Updating data over the internet is necessary for most apps. The http package has got that covered!
The following are the steps to take when updating Data over the internet in Flutter
- Add the http package.
- Update data over the internet using the http package.
- Convert the response into a custom Dart object.
- Get the data from the internet.
- Update the existing title from user input, update and display the response on the screen.
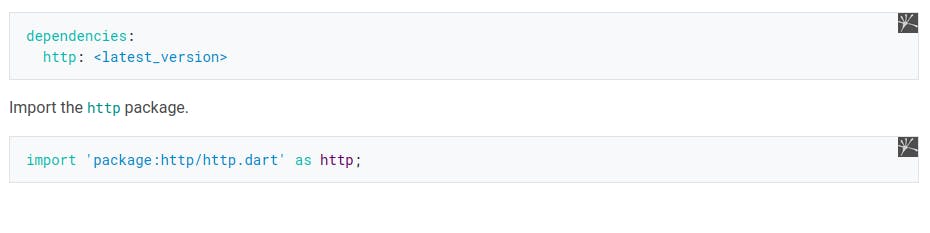
1. Add the HTTP package :
The first step always is to add your package to the popular pubspec.yaml as a dependency. Go to pub.dev to get HTTP package.
2. Updating data over the internet using the HTTP package.
Using the JSONPLACEHOLDER as our API, this is how to update Data over the internet.
Future<http.Response> updateAlbum(String title) {
return http.put(
Uri.parse('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/albums/1'),
headers: <String, String>{
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=UTF-8',
},
body: jsonEncode(<String, String>{
'title': title,
}),
);
}
3. Convert the http.Response to a custom Dart object.
While it’s easy to make a network request, working with a raw Future isn’t very convenient 😤. To make your life easier, convert the http.Response into a Dart object 😊😊
Create an Album Class First, create an Album class that contains the data from the network request. It includes a factory constructor that creates an Album from JSON.
This is how to create a class:
class Album {
final int id;
final String title;
Album({required this.id, required this.title});
factory Album.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return Album(
id: json['id'],
title: json['title'],
);
}
}
Then Convert the http.Response to an Album
Now, use the following steps to update the updateAlbum() function to return a Future:
Convert the response body into a JSON Map with the dart:convert package.
If the server returns an UPDATED response with a status code of 200, then convert the JSON Map into an Album using the fromJson() factory method.
If the server doesn’t return an UPDATED response with a status code of 200, then throw an exception. (Even in the case of a “404 Not Found” server response, throw an exception. Do not return null. This is important when examining the data in snapshot, as shown below.)
Future<Album> updateAlbum(String title) async { final response = await http.put( Uri.parse('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/albums/1'), headers: <String, String>{ 'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=UTF-8', }, body: jsonEncode(<String, String>{ 'title': title, }), ); if (response.statusCode == 200) { // If the server did return a 200 OK response, // then parse the JSON. return Album.fromJson(jsonDecode(response.body)); } else { // If the server did not return a 200 OK response, // then throw an exception. throw Exception('Failed to update album.'); } }
Hooray! Now you’ve got a function that updates the title of an album.
4. Get the Data from the Internet. Get the data from the internet before you can update it. For a complete example, see the Fetch data recipe on flutter.dev.
Future<Album> fetchAlbum() async {
final response = await http.get(
Uri.parse('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/albums/1'),
);
if (response.statusCode == 200) {
// If the server did return a 200 OK response,
// then parse the JSON.
return Album.fromJson(jsonDecode(response.body));
} else {
// If the server did not return a 200 OK response,
// then throw an exception.
throw Exception('Failed to load album');
}
}
Ideally, you will use this method to set _futureAlbum during initState to fetch the data from the internet.
5. Update the existing title from user input. Create a TextField to enter a title and a ElevatedButton to update the data on server. Also define a TextEditingController to read the user input from a TextField.
When the ElevatedButton is pressed, the _futureAlbum is set to the value returned by updateAlbum() method.
Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: TextField(
controller: _controller,
decoration: const InputDecoration(hintText: 'Enter Title'),
),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_futureAlbum = updateAlbum(_controller.text);
});
},
child: const Text('Update Data'),
),
],
);
On pressing the Update Data button, a network request sends the data in the TextField to the server as a POST request. The _futureAlbum variable is used in the next step.
5. Display the response on screen. To display the data on screen, use the FutureBuilder widget. The FutureBuilder widget comes with Flutter and makes it easy to work with async data sources. You must provide two parameters:
The Future you want to work with. In this case, the future returned from the updateAlbum() function. A builder function that tells Flutter what to render, depending on the state of the Future: loading, success, or error. Note that snapshot.hasData only returns true when the snapshot contains a non-null data value. This is why the updateAlbum function should throw an exception even in the case of a “404 Not Found” server response. If updateAlbum returns null then CircularProgressIndicator will display indefinitely.
FutureBuilder<Album>(
future: _futureAlbum,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.hasData) {
return Text(snapshot.data!.title);
} else if (snapshot.hasError) {
return Text('${snapshot.error}');
}
return const CircularProgressIndicator();
},
);
That it 🤔? Yes, that is it!!!
Note: You can choose where to updated the changes its sample codes are just for guidance on how you can effect an update.
If you would like to discuss this or any related issue Chat Me . Follow me on Twitter for More...
